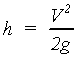(2-12)
CHAPTER 2 - BASIC CONCEPTS RELATED TO FLOWING WATER AND MEASUREMENT
A dropped rock or other object will gain speed rapidly as it falls. Measurements show that an object dropping 1 foot (ft) will reach a velocity of 8.02 feet per second (ft/s). An object dropping 4 ft will reach a velocity of 16.04 ft/s. After an 8ft drop, the velocity attained is 22.70 ft/s. This gain in speed or acceleration is caused by the force of gravity, which is equal to 32.2 feet per second per second (ft/s2). This acceleration caused by gravity is referred to as g.
If water is stored in a tank and a small opening is made in the tank wall 1 ft below the water surface, the water will spout from the opening with a velocity of 8.02 ft/s. This velocity has the same magnitude that a freely falling rock attains after falling 1 ft. Similarly, at openings 4 ft and 8 ft below the water surface, the velocity of the spouting water will be 16.04 and 22.68 ft/s, respectively. Thus, the velocity of water leaving an opening under a given head, h, is the same as the velocity that would be attained by a body falling that same distance. The equation that shows how velocity changes with h and defines velocity head is:
(2-12)
which may also be written in velocity head form as: